From the opulent darker tones of black walnut to the airy creamy whites of hard maple, the United States is home to an incredible variety of hardwood.
It’s also a superb source of sustainable timber (or, as they also like to call it across the pond, ‘lumber’). American hardwood forests are very well managed and, generally speaking, trees are growing at a rate faster than they are being felled, making them the ultimate eco-friendly construction material.
But as well as an abundance of hardwood, there’s also so much variety – in colour, character and grain pattern.
If you’re seeking a special US hardwood for your next project, or just looking to learn more about America’s arboreal offerings, here’s those you should know about.
Alder

Also known as: Red alder, Western alder
Scientific name: Alnus rubra
Origins: Pacific Northwest of the US, parts of Canada
Colour: Pale brown to reddish-brown, darkening with age
Grain: Straight, with a fine, even texture
Density: 530–690 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 2,600 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, musical instruments, veneers, plywood
The most commercially widespread hardwood hailing from the northwest of the US, alder is almost white when sawn, but darkens over time.
Whilst by no means the strongest or most scratch resistance of hardwoods – nor the most externally durable – alder has very good working properties. It’s a furnituremaking favourite.
Interestingly, alder’s oily smoke makes it the go-to timber for smoking salmon. The tree’s bark can be used to make dyes, and native Americans harnessed it for medicinal purposes.
The species also plays a role as an environmental indicator – its leaves develop discolouration in areas where there is a high level of ozone pollution.
Ash
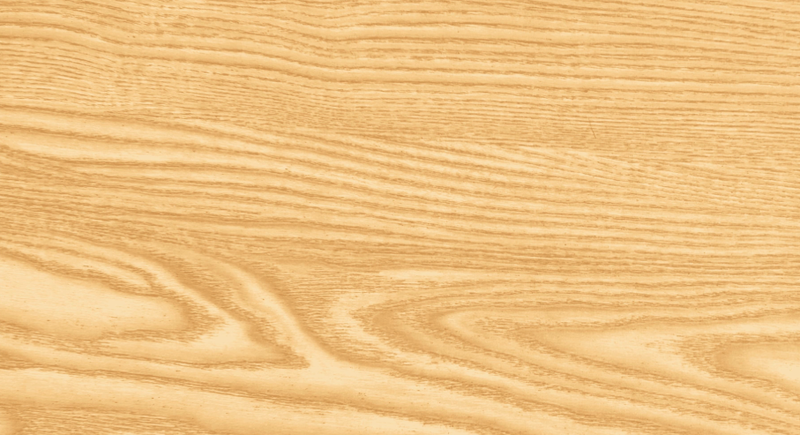

Also known as: American ash, white ash
Scientific name: Fraxinus americana
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Light brown to pale yellow with a hint of gray
Grain: Bold, straight, with occasional wavy patterns
Density: 700–900 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 5,900 N
Uses: Furniture, baseball bats, flooring, tool handles, musical instruments
Ash’s strength, bold straight grain, stability, working properties, wide availability and versatile pale colour make it a top choice for a range of projects, particularly flooring and furniture.
It is one of the most used trees in the US and is cultivated wherever possible. There are estimated to be over eight billion ash trees in the United States.
Along with alder, this hardwood is commonly used to create the body of musical instruments – it offers excellent resonance and tonal balance.

Basswood
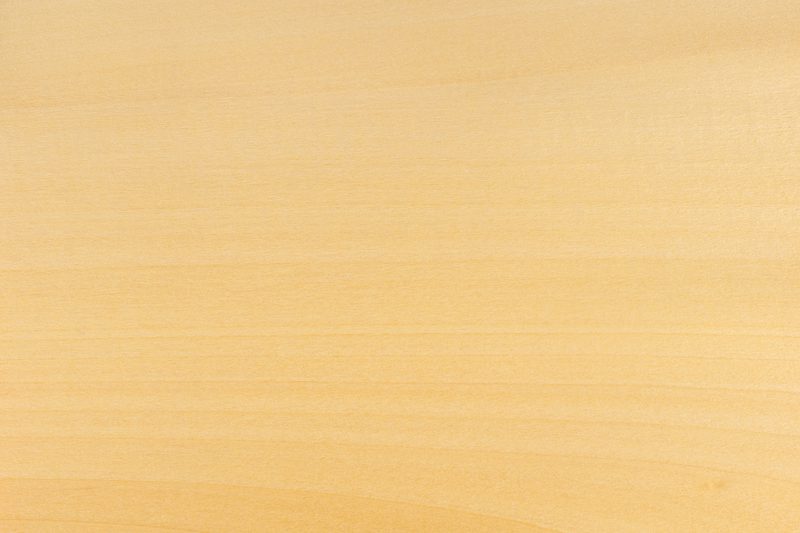

Also known as: American basswood, linden
Scientific name: Tilia americana
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Pale cream to light brown with a slight reddish hue
Grain: Straight, fine and even texture
Density: 370–510 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 1,800 N
Uses: Furniture, carving, musical instruments (such as guitar bodies)
Not all woods classified as ‘hardwoods’ are necessarily hard – as super-soft basswood demonstrates. Light and with soft strength properties and a fine and even texture, it’s perfect for wood carving, pattern-making, mouldings and musical instruments. The wood has great working properties, but can shrink if not dry.
Beech
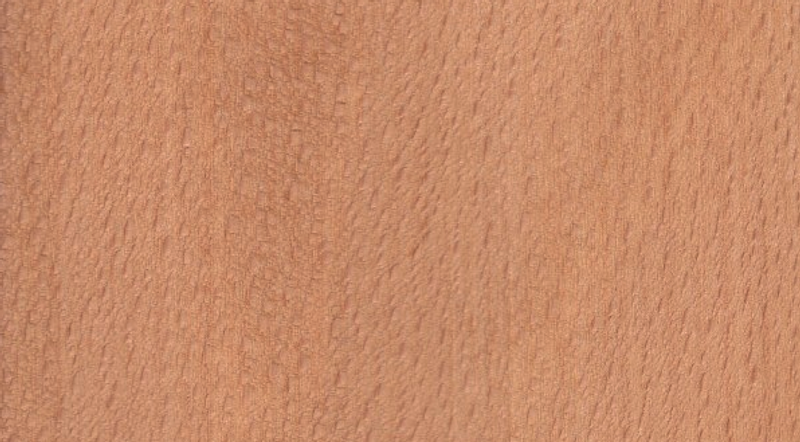

Also known as: American beech
Scientific name: Fagus grandifolia
Origins: Eastern and northeastern US
Colour: Light cream to reddish-brown
Grain: Straight, fine texture
Density: 720–800 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 5,800 N
Uses: Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, tool handles
Beech timber is a light cream to reddish-brown colour with a smooth, fine grain. Strong, tough and workable, it’s another favourite for flooring and furnituremaking, although it is not particularly durable outdoors.
Once around 40 years old, beech trees start to produce nuts, which are edible and can even be roasted, ground and used as a coffee substitute – the leaves are also edible. A complete meal!

Birch
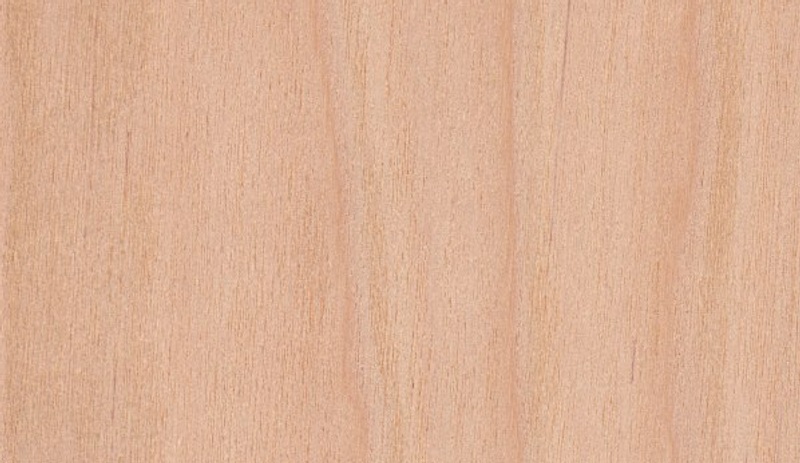

Also known as: Yellow birch, golden birch, swamp birch
Scientific name: Betula alleghaniensis
Origins: Northeastern US
Colour: Pale yellow to light reddish-brown
Grain: Fine, straight with a smooth texture
Density: 640–710 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 5,620 N
Uses: Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, plywood, veneers
While a provincial tree of Quebec in Canada, birch can be found throughout the northeast of the US, as far south as the Appalachian Mountains in northern Georgia. Its common names relate to the golden colour of the tree’s bark.
A mainstay of furnituremaking, doors and flooring, birch can also be tapped for its syrup.


Also known as: American cherry, black cherry, rum cherry
Scientific name: Prunus serotina
Origins: Midwestern and eastern US
Colour: Rich reddish-brown, darkens with age
Grain: Straight, fine texture
Density: 600–800 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 4,430 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, millwork, fine woodworking
Cherry’s rich pinkish-reddish tones, strength, working properties, fast-growing nature and widespread distribution make it one of the most distinctive American hardwoods.
The tree’s raw fruits are edible – they can also be made into jelly and the juice can be used as a drink mixer, hence the common name ‘rum cherry’.
Such is cherry’s beauty and historic exoticism for Europeans, it has been introduced in western and central Europe as an ornamental tree.

Also known as: Grey elm, red elm, slippery elm, soft elm
Scientific name: Ulmus rubra
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Light to medium brown with reddish hues
Grain: Straight to slightly interlocked, with a coarse texture
Density: 560–640 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 3,830 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, veneer, flooring, barrels
Reddish-dark brown in colour with green and purple flecks, elm offers a distinctive, warm look. It has good machining properties, is shock resistant and has an interlocked grain that makes it difficult to split – it has historic use in the making hubs of wagon wheels. Its inner bark is edible raw or cooked and can be used to make tea.

Hickory

Also known as: Shagbark hickory, mockernut hickory
Scientific name: Carya spp.
Origins: Eastern US
Colour: Light to medium brown with reddish tones
Grain: Straight, with a coarse texture
Density: 900–1,100 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 8,100 N
Uses: Tool handles, furniture, flooring, cabinetry
Hickory refers to a number of species from the genus Carya. Several species are distributed across Asia, and 12 are native to North America – the most popular example being shagbark hickory.
Hickory’s combination of strength, stiffness and shock resistance is unmatched by any other commercially-available wood – it is used in flooring and tool handles.
The tree is just as well known for its nuts, a rich source of B vitamins. Extracts from shagbark hickory’s bark is also widely used for syrup – similar to maple syrup.
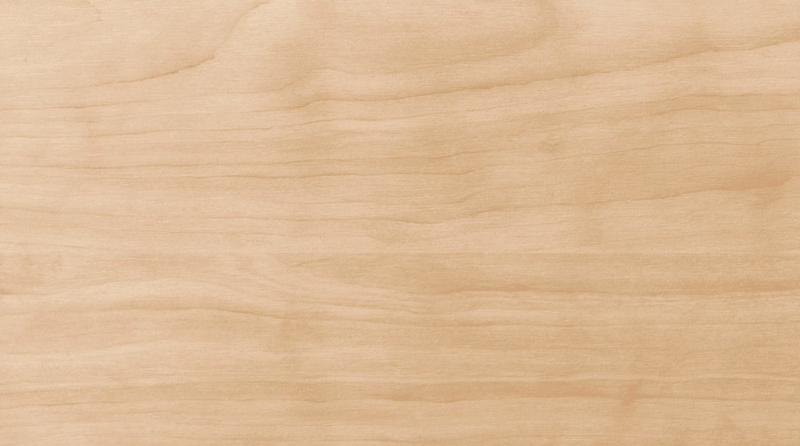


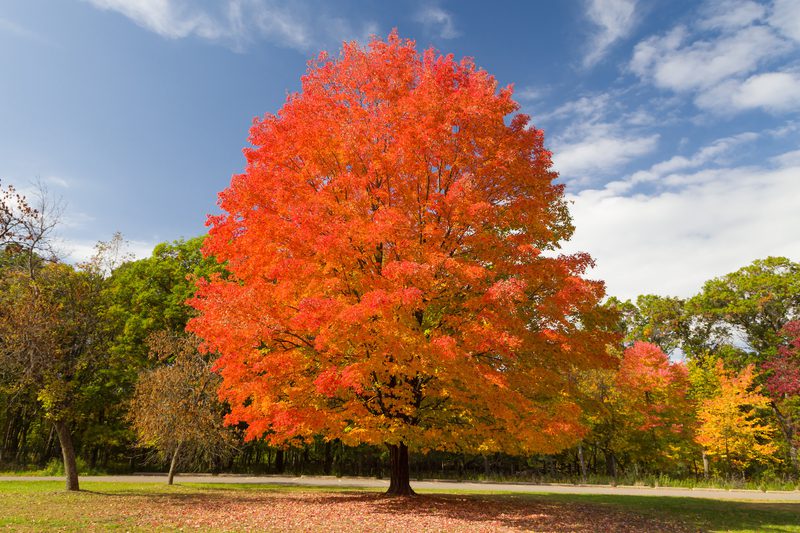
Also known as: Rock maple, sugar maple
Scientific name: Acer saccharum
Origins: North-east US and Canada
Colour: Creamy white, sometimes with golden or reddish tint
Grain: Straight and subtle
Density: 705-770 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 6,450 N
Uses: Furniture, flooring, kitchen, table tops
Hailing from the cold-weather climates of north-east US, maple’s uniform creamy whites make it a sought-after choice for any project where an airier, potentially Scandi-inspired look is desired.
It’s also incredibly dense, meaning superb resistance to knocks, bumps, scrapes and scratches. That’s not to mention that this species typically has a very straight grain and close, fine texture – a woodworker’s dream.
Wood enthusiasts cherish hard maple as it can occasionally be found with unique figuring – visual markings resulting from aberrations in how the wood grows. Common examples include ‘birds-eye’, ‘curly’ and ‘tiger stripe’.


Soft maple
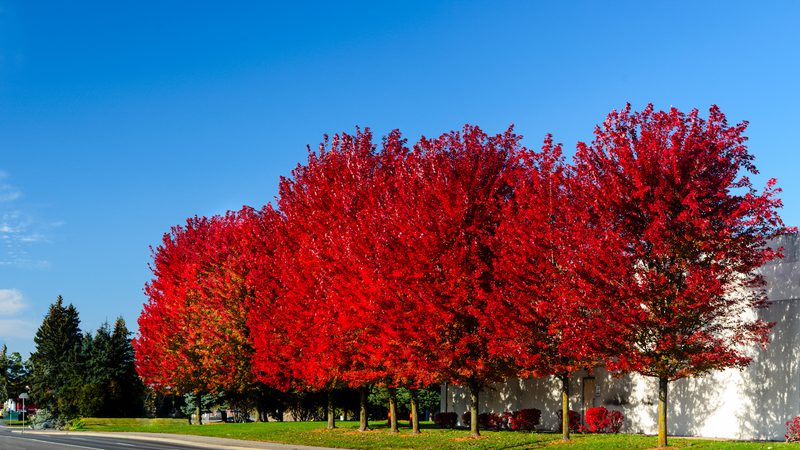
Also known as: Red maple, silver maple, swamp maple
Scientific name: Acer rubrum
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Light cream to reddish-brown
Grain: Straight, with some irregularity
Density: 580–640 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 4,200 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, veneer
Note that while the common name ‘hard maple’ refers to only one type of maple tree – Acer saccharum – ‘soft maple’ refers to a number of species, all with differing levels of strength, hardness and weight. The most popular soft maple species is Acer rubrum, red maple.
Lighter and softer than hard maple though it may be, soft maples are still pretty strong and dense! They tend to have a slighter darker colour, with more red and brown streaks.
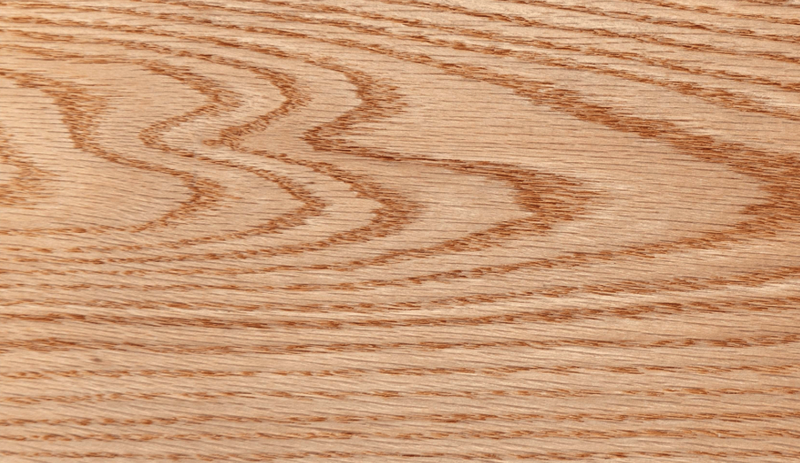


Also known as: American white oak
Scientific name: Quercus alba
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Pale to medium brown
Grain: Straight, with occasional flecking
Density: 770–800 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 6,000 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, flooring, wine barrels
An undisputed American icon and state tree of Illinois. White oak’s pale colour lends this wood its common name, although confusingly, there can sometimes be hints of red.
(It’s worth noting that while there are a number of types of white oak, the Quercus alba species is the one most associated with the name.)
Its immense size makes white oak a popular ornamental tree. The water and rot resistance of its wood makes it a go-to timber for wine and whisky barrels.
The wood works well, but make sure to use stainless steel fixings – iron will cause bleeding.

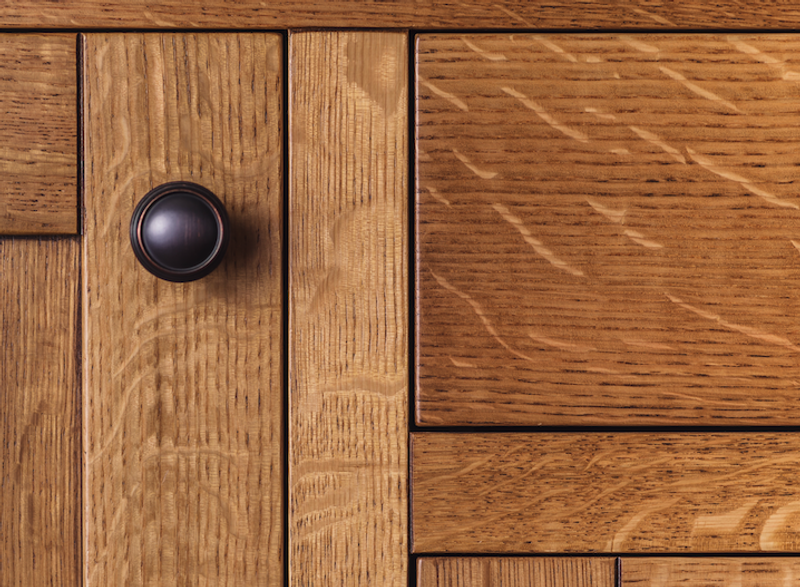
One of the most prized properties of oak is its grain pattern. When quarter sawn, white oak shows medullary rays – a unique cellular structure – which can produce an eye-catching ray fleck figuring on the wood’s surface, sometimes called ‘tiger oak’.

Red oak
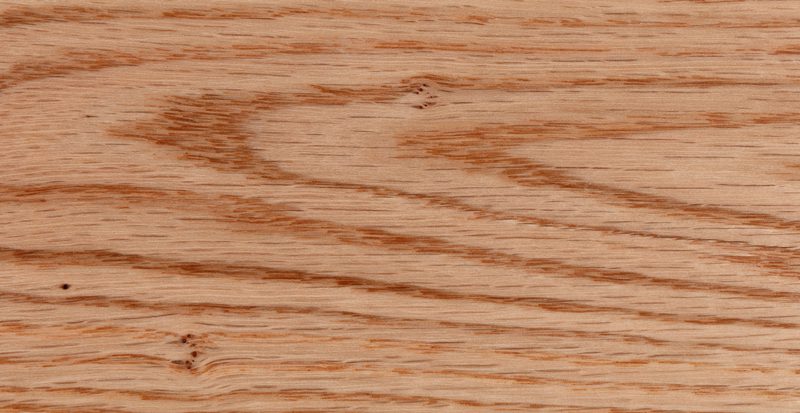

Also known as: Northern red oak, champion oak
Scientific name: Quercus rubra
Origins: Eastern and central US
Colour: Light to medium brown with a reddish hue
Grain: Straight with a coarse texture
Density: 700–900 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 5,700 N
Uses: Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, millwork
Another US cultural symbol, red oak is the state tree of New Jersey. It’s the most abundant tree growing in eastern US forests and is widely available.
Like white oak, the name ‘red oak’ can cover a number of species. However, it’s most associated with the Quercus rubra.
Red oak does tend to sometimes have a slightly paler and redder hue than white oak on average, but given the variation between trees, telling two pieces apart based on colour alone can be challenging.
A beautiful tree often used for ornamental purposes, red oak’s timber is similarly valued. It’s dense, naturally durable and has good working properties.
While quarter-sawn red oak does feature the ray fleck figure as those we discussed with white oak, it’s not typically as impressive.


Also known as: Tulip tree, tulip-poplar, yellow poplar, fiddletree
Scientific name: Liriodendron tulipifera
Origins: Eastern US
Colour: Pale yellow with greenish hues, sometimes streaked with brown or orange
Grain: Straight, with fine texture and occasional irregularities
Density: 450–500 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 2,450 N
Uses: Furniture, cabinetry, veneer, decorative woodwork
Even though it’s not part of the Populus genus and therefore is not a true poplar, it’s often referred to as ‘yellow poplar’ in the US – thought to be because of the visual similarities between tulipwood and true poplars.
Stable, fine grained, inexpensive and relatively soft (for a hardwood), it’s excellent for woodworking. Whilst pale yellow-green, the wood can have red, purple or even black streaks depending on the soil where it was grown.
It’s distributed across eastern North America: as far north as Ontario, as far south as central Florida and as far west as Illinois. As one of the tallest trees native to temperate regions – reaching as tall as 50m – it’s a beautiful tree for landscaping.
Tulipwood is also one of the largest honey plants in the eastern US – nectar is produced in the orange part of its flowers.
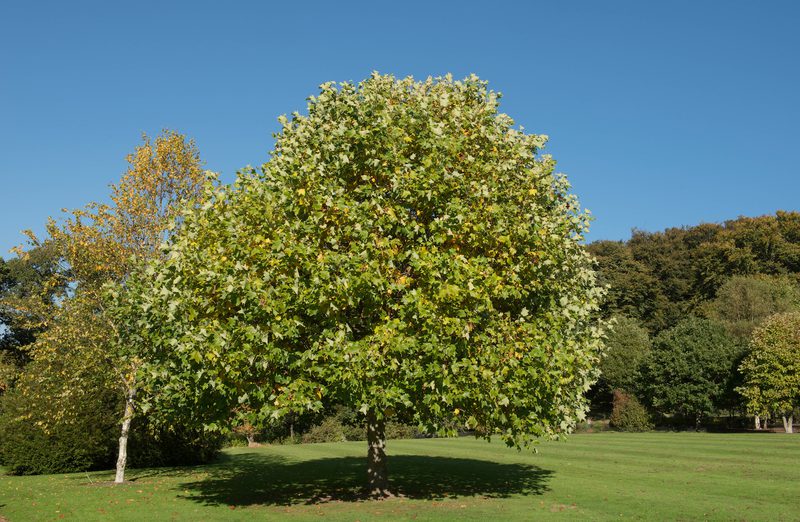
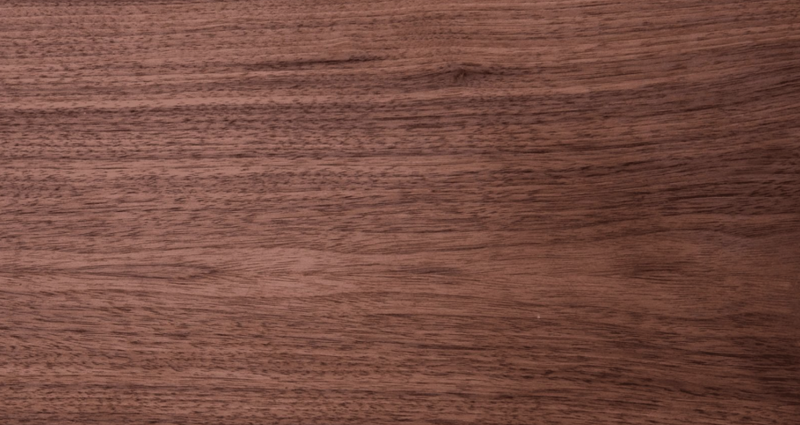


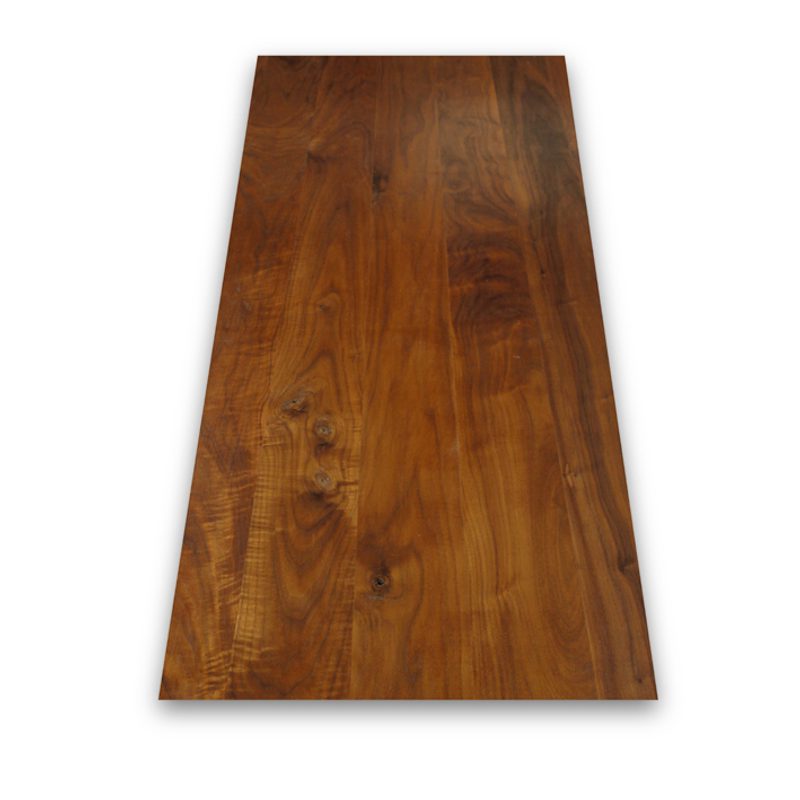
Also known as: Black walnut, eastern American black walnut
Scientific name: Juglans nigra
Origins: Eastern US
Colour: Dark brown with a purplish hue and light brown streaks
Grain: Straight, with occasional curls
Density: 640–750 kg/m³
Janka hardness score: 4,480 N
Uses: Fine furniture, flooring, cabinetry, veneers
Walnut’s darker brown colour with hints of purple works well in contrast with lighter colours and pale woods – a commercially prized timber for projects that might benefit from a luxurious, opulent touch.
While mainly straight grained, walnut can have some interesting figuring, such as occasional waves and curls. The wood works very easily – machining, nailing, screwing, glueing and finishing don’t generally present any problems.
That’s not to mention the trees bear edible nuts, popularly used in ice cream and baked goods. Black walnut trees also yield a sap that can be used for syrup and sugar, not unlike maple. Walnut’s drupes also contain compounds that are also used to create dyes for a variety of staining applications.



Popular American softwoods
It’s not all about hardwoods. Honourable mention must go to those commercially-popular American softwoods, too: western red cedar, Douglas fir, eastern white pine and southern yellow pine (to name but a few). These are predominantly distributed across the Pacific Northwest – northwestern US and southwestern Canada.


Both Western red cedar and Douglas fir are great examples of how common names can cause confusion. Cedar is actually of the Thuja genus, meaning it’s not a true cedar (Cedrus genus), and fir is of the Pseudotsuga genus, rather than the Abies genus.
While they may lack in terms of density and scratch resistance, these types of wood often have very good natural durability, giving them widespread application outdoors, for example on cladding or fencing projects.
If you were confused about the differences between hardwood and softwood, there’s no need to be embarrassed – we’ve written an entire blog post breaking down the differences.
Duffield Timber: your one-stop shop for a world of wood
Rather than simply reading about these terrific types of timber, why not see them for yourself?
If you’re nearby, come and take a look around our woodworking shop. Affectionately named the ‘hobby hall’, it’s a treasure trove of imported wood from across the world – including many of the species listed in this article. We’re located just off the A1, in Melmerby, near Ripon, North Yorkshire.
If you’re working on a project and need some advice, or you’re after a specific type of wood, don’t hesitate to drop our team a message. We’d be delighted to help.
PS: If you enjoyed this article, don’t miss our guide to African hardwoods!







